The Role of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Developers

Virtualization is the technology that made cloud computing possible. For decades, each application required its own dedicated physical server. When virtualization came on the scene, it taught computers how to share space like civilized roommates. It’s the unsung hero behind the cloud, transforming rigid hardware into flexible, shareable resources and enabling instant scalability and cost-efficiency.
Initially, a niche for mainframe partitioning, virtualization evolved with advances in hypervisors, leading to broader enterprise adoption. Due to the growing demand for scalable, cost-effective IT solutions, virtualization became the backbone of cloud infrastructures, enabling rapid provisioning, multi-tenancy, and efficient utilization of large-scale data centers.
What is virtualization?
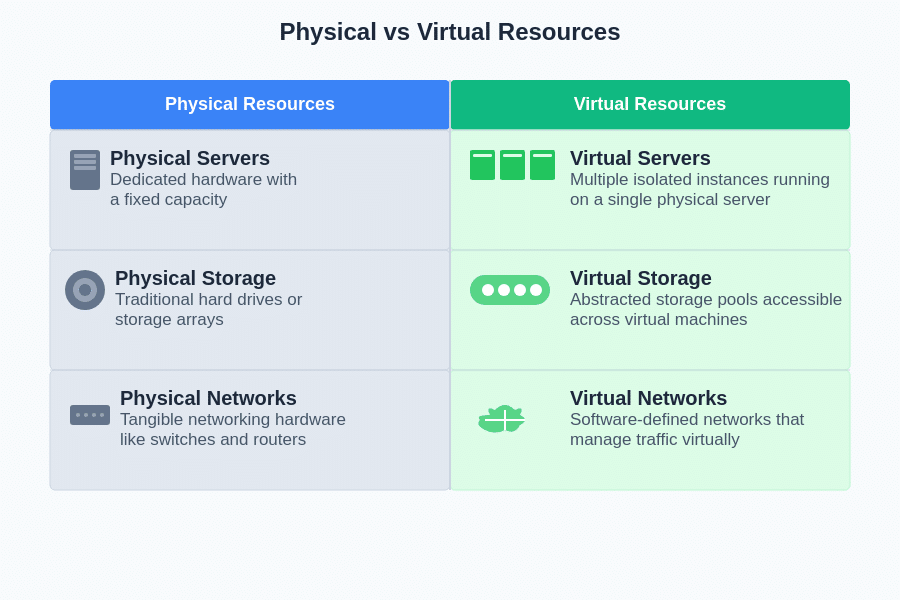
Virtualization is a technology that enables the creation of multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from a single physical hardware system. It allows one physical server to run several independent operating systems or applications simultaneously, optimizing hardware utilization and increasing flexibility. Virtualization abstracts the physical hardware, presenting it as a set of virtual components like servers, storage, and networks.
Abstraction in virtualization is the process of separating physical hardware from the operating system and applications. It creates a virtual layer that allows software to interact with virtual representations of physical components, without needing to know the specifics of the underlying hardware. This makes resource management more efficient and scalable.
Here’s a breakdown of physical and virtual resources:
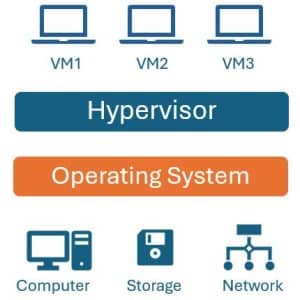
At the heart of virtualization is the hypervisor, a piece of software that creates and manages virtual machines (VMs). It works by dynamically allocating the underlying physical hardware. Hypervisors are classified into two primary types:
Type 1, bare metal, runs directly on hardware.
Type 2, hosted, runs on an existing OS. They enable isolation, resource distribution, and simplified management of VMs.
Types of virtualization
The main types of virtualization include:
- Server virtualization divides a physical server into multiple virtual servers using software called a hypervisor. Each virtual server uses its own operating system, improving hardware utilization and scalability.
- Storage virtualization combines multiple physical storage devices into a single virtual storage pool. This allows centralized management, better data availability, and easier backup and recovery.
- Network virtualization abstracts physical network resources like switches and routers into a virtual network. It enables flexible network management, improved security, and efficient traffic control without changing the underlying hardware.
- Desktop virtualization allows users to access a cloud desktop environment hosted on a central server. This helps in managing multiple user desktops centrally, improving security and simplifying maintenance.
- Application virtualization separates applications from the underlying operating system, allowing them to run in isolated environments. This makes deploying, updating, and managing applications easier while reducing conflicts and compatibility issues.
Together, these virtualization types support efficient resource use, reduce costs, and enhance scalability and disaster recovery, making them critical in modern IT infrastructure.
How virtualization powers cloud computing
Cloud providers use virtualization to efficiently create, manage, and allocate computing resources to users on demand. By virtualizing physical hardware, such as servers, storage, and networks, they can run multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server using hypervisors. This enables optimal use of hardware and supports multitenancy, where multiple users share the same infrastructure securely.
Virtualization allows cloud providers to quickly scale resources up or down based on user needs, ensuring flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Storage virtualization helps manage data across various physical devices as a unified system, improving data access and backups. Network virtualization creates isolated virtual private clouds for clients who need enhanced security and control.
Overall, virtualization is the backbone of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing, enabling dynamic resource provisioning, efficient workload distribution, and high availability. It allows cloud providers to deliver reliable, scalable, and customizable services to users worldwide.
Resource pooling and allocation
Resource pooling and allocation are core principles of cloud computing that enable efficient use of computing resources.
Resource pooling means that cloud providers group together physical resources, such as servers, storage, and networks, and share them among multiple users using virtualization. This creates a large pool of resources that can be dynamically assigned based on demand.
Resource allocation is the process of distributing these pooled resources to users or applications as needed. Virtual machines (VMs), containers, or other virtual instances are created and allocated specific portions of CPU, memory, and storage based on user requirements or service-level agreements (SLAs).
This approach ensures better hardware utilization, scalability, and cost-efficiency. Users get the resources they need without owning the infrastructure, while providers maximize resource use. Automated tools often manage allocation to ensure optimal performance, balance workloads, and support high availability. Together, pooling and allocation form the foundation of flexible and efficient cloud service delivery.
How does virtualization enable on-demand scalability?
Virtualization enables on-demand scalability by allowing cloud providers to create and manage virtual instances of computing resources quickly and efficiently. Instead of relying on fixed physical hardware, virtualization uses hypervisors to run multiple environments on a single virtual dedicated server. This flexibility allows resources like CPU, memory, and storage to be allocated or reallocated dynamically based on current demand.
When a user or application needs more computing power, additional VMs or containers can be rapidly deployed from the virtual resource pool without requiring new physical hardware. This makes scaling up (adding resources) or scaling down (reducing resources) seamless and fast.
Virtualization also supports automated scaling tools that monitor workloads and adjust resources in real-time, ensuring optimal performance. This is especially useful for handling traffic spikes or growth in usage. Overall, virtualization enables efficient, cost-effective, and responsive scaling, which is essential for modern cloud computing environments and dynamic business needs.
Benefits of virtualization in the cloud
Virtualization offers numerous benefits that significantly enhance IT infrastructure efficiency and resilience.
- One of the most notable advantages is cost savings. By consolidating multiple virtual machines (VMs) onto fewer physical servers, organizations reduce hardware acquisition and maintenance costs. Additionally, energy consumption drops, leading to lower utility bills and a greener footprint.
- Virtualization also enhances scalability and flexibility; it allows businesses to easily allocate or scale resources based on demand, enabling quick adaptation to changing workloads or growth.
- Improved resource utilization is another key benefit, as virtualization maximizes the use of physical hardware by dynamically allocating computing resources among VMs, avoiding the inefficiencies of underused servers.
- This optimization also contributes to faster deployment and provisioning. New virtual machines or environments can be created in minutes, accelerating development and testing cycles.
- Enhanced reliability and availability are achieved through features like live migration and automatic failover.
- In case of failures, virtualization supports robust disaster recovery and business continuity strategies by enabling fast backups, snapshots, and VM replication across sites.
Overall, virtualization empowers organizations to operate more efficiently, reduce costs, and ensure robust, adaptable, and resilient IT environments.
Bottom line
Virtualization innovation is the foundation of cloud service development. It enables the abstraction of physical hardware, allowing multiple virtual machines to run on a single server. This efficiency drives the scalability, flexibility, and resource pooling essential for cloud computing.
Through virtualization, cloud providers can offer on-demand services, rapid provisioning, and cost-effective infrastructure. Ultimately, advances in virtualization technologies have made cloud services more reliable, accessible, and scalable, powering the growth of public, private, and hybrid cloud environments.
